Are you experiencing hair loss and unsure of the cause? Hair loss is often linked to autoimmune diseases, which can be a frustrating and confusing experience. This guide breaks down how autoimmune diseases can lead to hair loss and offers potential treatments to help you regain confidence in your appearance.
Let’s dive in and find answers to some of your questions.

Understanding Hair Loss and Autoimmune Disease: Causes & Treatments
Losing hair without a clear cause can be incredibly frustrating. For many, autoimmune diseases are at the root of the issue, as these conditions cause the body to mistakenly attack its own tissues—including hair follicles. Knowing more about these conditions can help you take control of your hair health.
1. Introduction to Hair Loss and Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly targets healthy tissues, including hair follicles, resulting in conditions like alopecia areata and lupus that can lead to significant hair loss. Millions of people live with these conditions, making it essential to understand potential solutions.
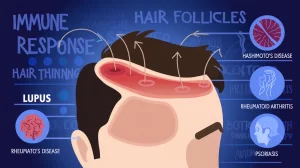
2. Overview of Autoimmune Diseases That Cause Hair Loss
Lupus
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes inflammation throughout the body, including the scalp. There are two main types that affect hair: systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), which often leads to non-scarring alopecia, and discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), which can cause scarring on the scalp and more severe hair loss.
- Diagnosis: Lupus-related hair issues are often diagnosed with blood tests and Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF), which helps differentiate DLE from other conditions.
- Treatment: Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants are common treatments that help manage symptoms and support hair regrowth.
Hashimoto’s Disease
Hashimoto’s disease affects the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism, which slows metabolism and impacts hair growth. It is more common in women and causes symptoms like fatigue, dry skin, and hair thinning.
- Complications: Left untreated, it can lead to severe complications like goiter or mental health issues.
- Treatment: Early diagnosis and thyroid hormone replacement therapy are crucial for managing hair loss related to Hashimoto’s disease.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
While rheumatoid arthritis primarily affects the joints, it also causes systemic inflammation that can impact hair growth. Medications commonly used for RA, such as methotrexate and leflunomide, may contribute to hair loss as a side effect.
- Treatment Options: RA treatment includes biologic drugs and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, which help manage both RA and conditions like alopecia areata, though these treatments sometimes come with hair-related side effects.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis affects around 7.5 million people in the U.S., with many experiencing scalp psoriasis, which produces flaky or scaly patches that can obstruct hair follicles.
- Symptoms: Symptoms range from mild dandruff-like flaking to severe plaques.
- Treatment: Scalp psoriasis is managed with topical treatments, UV light therapy, and systemic medications to reduce inflammation and promote scalp health.
Common Symptoms of Hair Loss Due to Autoimmune Disorders
Patchy Hair Loss
Patchy hair loss is a characteristic symptom of autoimmune-related hair loss, especially in conditions like alopecia areata, which affects nearly 7 million people in the U.S. This type of hair loss often appears suddenly as small, round bald spots on the scalp.
Scalp Inflammation and Soreness
Scalp inflammation and tenderness are common in autoimmune disorders due to the immune system attacking healthy cells. Conditions like discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) and scalp psoriasis often present with these symptoms, which can lead to irreversible hair loss if untreated.
Progressive Thinning
Progressive thinning occurs gradually and may eventually lead to complete baldness in severe cases like alopecia totalis or universalis. This type of hair loss is often due to long-term inflammation that affects the hair follicles’ health and ability to regrow hair.
Diagnosis and Tests for Hair Loss in Autoimmune Diseases
Proper diagnosis is essential for managing autoimmune-related hair loss. Doctors use several tests to identify the specific cause and determine an appropriate treatment plan.
Blood Tests
Blood tests help identify markers of inflammation and autoimmune activity. They often measure ferritin (iron storage), hormone levels, and other indicators linked to hair loss conditions like alopecia areata or Hashimoto’s disease.
Scalp Biopsy
A scalp biopsy is performed by taking a small tissue sample from the scalp to examine hair follicles and detect specific autoimmune conditions. This test can differentiate between similar conditions, such as lichen planopilaris and lupus, which may require different treatments.
Treatment Options for Hair Loss from Autoimmune Diseases
Managing hair loss from autoimmune diseases can be challenging, but several treatment options are available to help reduce inflammation, regulate the immune system, and encourage hair regrowth.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system, which helps prevent the immune attack on hair follicles. Common corticosteroids include betamethasone, prednisolone, and methylprednisolone, which are available in intravenous and oral forms.
- Side Effects: Possible side effects include weight gain and mood changes, so these are often combined with other drugs like methotrexate for severe cases.
Immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressants calm the immune system, which can slow or stop the immune attack on hair follicles in conditions like alopecia areata.
- Medications: Systemic corticosteroids, JAK inhibitors (such as ruxolitinib and tofacitinib), and other drugs like methotrexate are effective in controlling symptoms and promoting hair growth.
- Usage: Long-term treatment is often necessary for persistent cases.
Biologic Drugs
Biologic drugs are a newer treatment option that targets specific parts of the immune system to treat autoimmune-related hair loss. The FDA has approved JAK inhibitors like baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and deuruxolitinib for severe cases of alopecia areata, with baricitinib showing significant regrowth results in clinical trials.
- Adolescents: Ritlecitinib was approved as a treatment option for adolescents aged 12 and older, expanding access to younger patients dealing with alopecia areata.
Conclusion
Understanding the link between autoimmune diseases and hair loss is essential for managing symptoms effectively. Conditions like lupus, Hashimoto’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis can cause or contribute to hair loss. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment—such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologic drugs—individuals with autoimmune-related hair loss can take steps toward managing symptoms and improving hair growth.
Summary Points
- Autoimmune Conditions and Hair Loss: Diseases like lupus, Hashimoto’s, and psoriasis can lead to hair loss by attacking hair follicles.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include patchy hair loss, scalp soreness, and progressive thinning.
- Diagnosis: Blood tests and scalp biopsies help identify underlying causes and guide treatment.
- Treatment Options: Available treatments include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologic drugs, all aimed at reducing immune attacks on hair follicles.